Solar & Renewable Energy
Efficient maintenance of solar parks
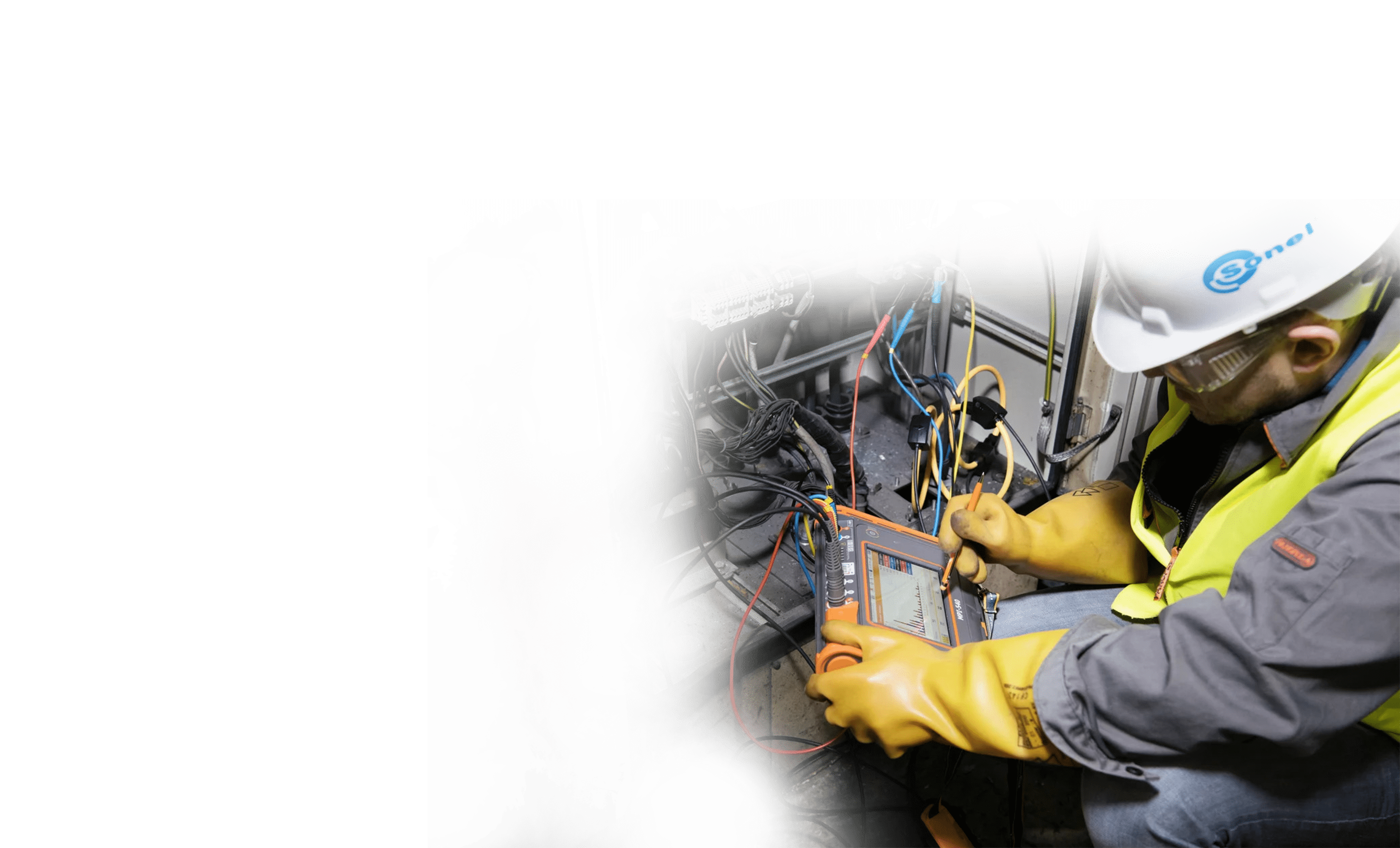
Regular thorough examinations are especially important for large photovoltaic facilities, as a single solar cell failure might already have a detrimental impact on the whole yield.
Measurement of time savings:
Solar thermography is a very efficient approach for searching for thermal anomalies, even with hundreds of square metres of module area and fluctuating solar irradiation intensity.
The solar radiation intensity value can be saved alongside the thermal image and used for image analysis later.

Solar Energy
Solar energy is a type of renewable energy that comes from the sun. It is harnessed using various technologies, such as solar panels (photovoltaics), solar thermal systems, and concentrating solar power systems. Solar energy is abundant and inexhaustible, making it a key player in the transition towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources.
Photovoltaics (PV): Photovoltaic cells, commonly known as solar cells, convert sunlight directly into electricity. Solar panels are made up of these cells and are commonly used on rooftops or in solar farms.
Solar Thermal Systems: These systems use sunlight to generate heat, which can then be used to produce electricity or provide hot water for residential and industrial use.
Concentrating Solar Power (CSP): CSP systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a small area, generating heat that is then used to produce electricity.
Net Metering: Many solar installations are connected to the power grid, allowing excess electricity generated during sunny periods to be fed back into the grid, and the user is often credited for this surplus energy.


Advantages of Solar Energy
Clean and Renewable: Solar energy is a clean and sustainable source of power, producing little to no air or water pollution during operation.
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Solar power reduces reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
Low Operating Costs: Once solar panels are installed, the operational and maintenance costs are relatively low compared to traditional energy sources.
Job Creation: The growing solar industry creates job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research.
Decentralized Energy Source: Solar panels can be deployed on a small scale, providing decentralized energy solutions and reducing the need for extensive power distribution infrastructure.
Challenges
Intermittency: Solar power generation depends on sunlight, which is intermittent. Energy storage solutions and grid integration are needed to address this challenge.
High Initial Costs: While the operational costs are low, the initial investment in solar technology can be relatively high, although costs have been decreasing over time.
Land Use Concerns: Large-scale solar installations may require significant land area, potentially leading to conflicts with agriculture or natural habitats.
Applications
Residential Solar Power
- Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Panels: Installed on rooftops to generate electricity for residential use.
- Solar Water Heaters: Used for heating water for domestic purposes.
Our expertise in the field
Having a comprehensive understanding of these aspects ensures a well-rounded expertise in the field of residential solar power. This expertise not only involves the technical aspects of system design and installation but also extends to customer education, regulatory compliance, and ongoing system maintenance.
Emergency and Disaster Response
Solar-Powered Emergency Shelters: Solar energy is used to provide power in emergency shelters and disaster-stricken areas where traditional power sources may be disrupted.
Our expertise in the field
Expertise in emergency and disaster response requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining technical skills, effective communication, strategic planning, and a deep understanding of the communities being served. Continuous training, collaboration, and staying informed about the latest technologies and best practices are essential for professionals in this field.
Solar Street Lights
Outdoor Lighting: Solar-powered street lights and outdoor lighting systems that use photovoltaic panels to store and provide energy for illumination.
Our expertise in the field
A holistic approach that combines technical expertise, environmental consciousness, and community engagement is essential for success in the field of solar street lights. This includes staying updated on advancements in solar technology, lighting design, and sustainable practices to deliver effective and efficient solutions.