Research & Development
Measuring solutions for Research and development
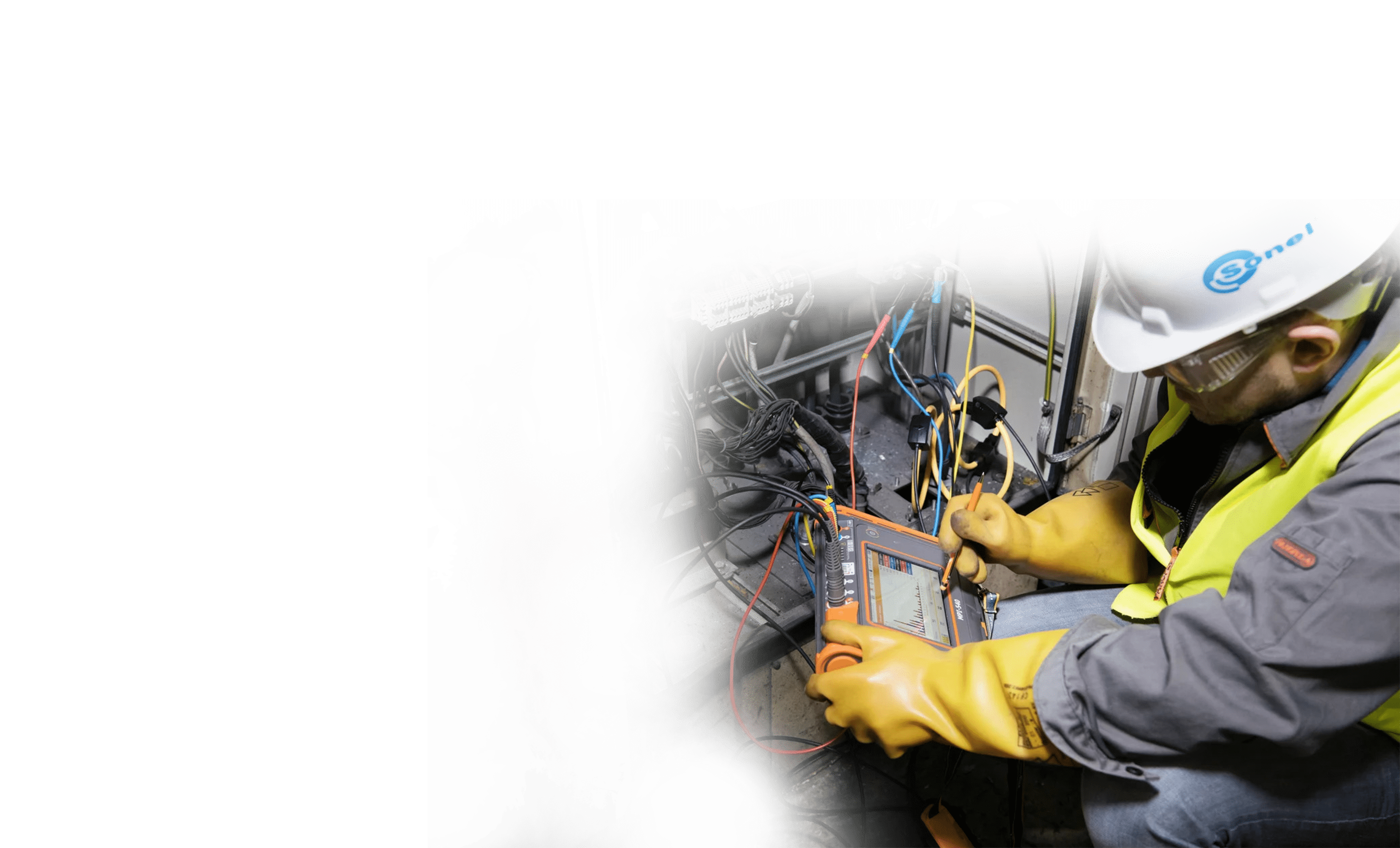
In research and development, professional mesuring technology can be useful in many cases. Temperatures and temperature profiles of complex processes can be analysed and documented simply and reliably using thermography. Thanks to indoor climate monitoring in measurement rooms, you avoid the smallest deviations before the start of series manufacturing.
In industry, the wrong ambient climate can damage sensitive materials and goods, and cause costs.
Use our climate monitoring system Assure the correct climate in measurement rooms.

Research & Development Objectives
R&D refers to the investigative activities that a business or organization conducts with the intention of making discoveries that can lead to the development of new products, processes, or services.
- Innovation: R&D aims to create and enhance products, services, or processes to stay competitive and meet evolving market demands.
- Cost Reduction: R&D may focus on finding more efficient ways of conducting operations or developing products, leading to cost savings.
- Problem Solving: R&D often addresses challenges or issues faced by the company, seeking solutions through research and experimentation.
- Market Expansion: R&D can explore new markets and opportunities for growth through the development of novel offerings.


Key Components
- Basic Research: Exploration of scientific principles and phenomena to expand knowledge without a specific practical application in mind.
- Applied Research: Use of existing knowledge to address specific problems or develop new products.
- Development: Translating research findings into practical applications, prototypes, or marketable products.
R&D Process
- Idea Generation: Brainstorming and identifying potential areas for research and innovation.
- Feasibility Study: Assessing the viability and potential success of the proposed projects.
- Research Planning: Defining the scope, objectives, and methodology of the research.
- Data Collection: Conducting experiments, surveys, or other activities to gather relevant information.
- Analysis: Analyzing data to draw conclusions and make informed decisions.
- Prototyping: Developing prototypes or models to test and validate ideas.
- Testing: Rigorous testing to ensure the reliability and functionality of the developed concepts.
- Implementation: Bringing successful projects to market or integrating new processes within the organization.
Applications
Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare
- Drug Discovery: R&D is crucial for discovering and developing new pharmaceuticals, improving existing medications, and advancing medical treatments.
- Medical Devices: Innovation in medical devices, diagnostics, and healthcare technologies to enhance patient care and outcomes.
Our expertise in the field
If you have expertise in the pharmaceuticals and healthcare field, your knowledge likely encompasses a range of areas related to drug development, medical research, healthcare technologies, and regulatory compliance. Here are key aspects where your expertise might be focused
Technology and Electronics
- Product Development: R&D is fundamental to creating new technology products, improving features, and staying ahead in the competitive tech market.
- Software Development: Research contributes to the development of new algorithms, software applications, and programming languages.
Our expertise in the field
Your expertise in these areas contributes to the advancement of technology and electronics, shaping the industry’s landscape and driving innovation across various sectors. It involves a dynamic combination of hardware and software skills, coupled with a deep understanding of emerging technologies and their applications.
Energy and Environmental Sciences
- Renewable Energy: Research in the development of renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and bioenergy.
- Environmental Conservation: R&D for sustainable practices, waste reduction, and pollution control.
Our expertise in the field
Your expertise in these areas contributes to the development and implementation of sustainable solutions, addressing the challenges posed by energy needs and environmental conservation. It involves a multidisciplinary approach, combining scientific knowledge with policy understanding and community engagement.